Abstract
BACKGROUND
The use of immunosuppressive agents such as antithymocyte globulin (ATG) as graft-versus host disease (GVHD) prophylaxis may increase the risk of Epstein Barr Virus (EBV) related post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder (PTLD). The aim of the present study is to report the incidence, risk factors, and outcome of PTLD in the setting of haploidentical stem cell transplant (haploSCT) combining PTCy and ATG as GVHD prophylaxis.
METHODS
From August 2016 to May 2018, 55 adult patients diagnosed with hematological malignancies underwent T-cell replete haploSCT. All patients received a reduced intensity conditioning regimen (RIC) with fludarabine, busulfan, and 200cGy of total body irradiation (TBI), combined with rabbit ATG, PTCy and cyclosporine (Cy).
EBV titre was monitored by quantitative PCR in plasma samples. The cut-off value for test positivity was >600 copies of EBV DNA per milliliter of plasma. Testing was performed weekly from engraftment to day 100 and beyond in case the patients were on immunosuppression.
Data was collected through retrospective chart review. Last follow up was updated in June 31, 2018. Median follow-up was 9.5 months (range 1-21).
RESULTS
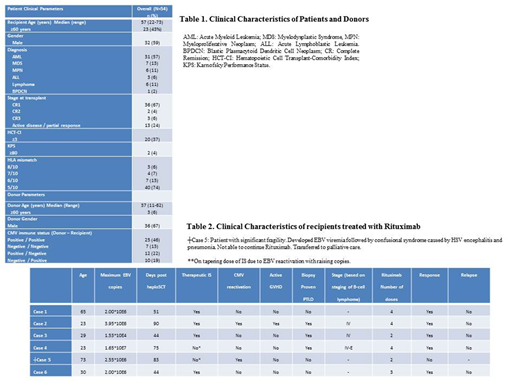
Patient and donor characteristics are summarized in Table 1. Median age was 57 (22-73) years, with 23 (43%) patients ≥60 years. Overall survival of the 55 patients at 6 months was 70% (95% CI 57-83), and 51% (95% CI 46-66) at 1 year.
EBV reactivation was documented in 31 (57%) patients. Median time to EBV reactivation was 54 (20-326) days. Three (5.5%) patients developed presumed PTLD with EBV-viremia higher than 1x10E6 copies and corroborative imaging. Three (5.5%) had biopsy-proven PTLD (Table 2). Median time since EBV reactivation to presumed/proven (P/P)-PTLD was 25 (3-36) days. All cases occurred early post-transplant within the first 100 days. Four patients were on therapeutic doses of cyclosporine. All 6 (11%) patients received treatment with weekly Rituximab 375 mg/m+. Five (83%) patients achieved complete clinical responses with PCR negativity with reduction of immunosuppression and single agent rituximab. One patient died of complications of viral encephalitis and bacterial pneumonia.
CONCLUSION
ATG based conditioning can be associated with increased viral reactivations. Frequent EBV monitoring and pre-emptive treatment may lead to rapid disease control. While no guidelines exist currently, further investigation is needed to define optimal monitoring strategies.
Lipton:BMS: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.